In agriculture, plants that grow in an undesirable location are called weeds. These plants typically grow quite quickly and are stubborn. Weeds typically outgrow and choke other cultivated plants. They compete with the desired or cultivated crops for minerals, light, and water, impacting agricultural productivity.
While many weeds are undesirable, some of them can actually be useful in your garden. The advantages and disadvantages of weeds will be discussed in this article to help you decide whether to keep or remove the weeds in your garden.
If you are interested in this topic , you can also read
<<Marigold Flower Benefits>> and <<Fig Leaf Benefits>>articles.
Benefits Of Weeds
Almost everywhere, weeds can grow, but if you know how to exploit these plants, you can use them to your advantage. In fact, you might be surprised to learn that sometimes advantages of weeds outweigh their disadvantages. Below are some of the benefits of weeds:
Improving Soil Quality
In the first place, weeds provide a layer of protection for the soil. Bare soil is vulnerable to erosion from wind, rain, and other natural forces.
Additionally, weeds can enrich the soil with essential nutrients, particularly if the soil has been left fallow for a time. The absence of organic matter and crucial nutrients is likely in soil that has been disturbed by human activity or extreme weather conditions like fires or floods. Weeds are among the first plants to reappear and start enriching and nourishing your soil.
You can use less manure because weeds decay where they grow and produce humus. They can also aid with soil moisture retention.
In contaminated waters, some weeds, like the water hyacinth, can absorb a variety of heavy metals. These plants can be ground up and used as compost for other plants [1].
Good For Wildlife
One of the advantages of weeds is that they benefit animals and wildlife in various ways. Insects, worms, and other soil-dwelling creatures can find food and shelter in weeds. In addition, they are a significant food source for birds.
Attracting Pollinators
Pollinators can be quite helpful in promoting the growth of plants. Weeds aid in pollination since they are advantageous to insects and other species. Bees, butterflies, and other pollinators are drawn to several weeds.
However, weed killers and pesticides can harm these pollinators, which are vital to our ecology.
Edible And Nutritious [2]
One of the amazing benefits of weeds is that some are so healthy and even edible. Many can be included in foods, including salads, drinks, and smoothies. Daisies, chickweed, and dandelion, for instance, are all edible. In some regions of the world, some are even used medicinally!
However, many weeds have similar-looking plants that shouldn’t be consumed so, it’s crucial to confirm that you have recognized the right plant. Additionally, you should always seek medical advice before using weeds as a kind of treatment since some people may experience adverse effects or allergic responses.
Aesthetic Appeal
Some weeds have a pleasing aesthetic quality and can be utilized to improve the garden visually.
Forage For Livestock
Various weeds can be used as pasture crops, including Bromus unioloides (Rescue grass), Hordeum murinum (Mouse barley or Wild barley), and Erodium cicutarium. It’s crucial to remember that animals should consume all of these plants before they set seed [3].
Natural Medicine
Many weeds are frequently employed in medicine; this may be because of the numerous secondary metabolites which their ruderal nature causes them to create. Both conventional and modern medicine take advantage of these metabolites. For example, broadleaf plantain can be used to minimize swelling. Additionally, nettle stings can be soothed with dock leaves [4].
Commercial Purposes
One of the surprising benefits of weeds is their economic advantages. For instance, Saccharum specie is a money-making weed that can be supplied to thatch producers.
Other weed species may contain high-quality oil that can be harvested and sold to make money. For example, Tagetes minuta weed has a pleasant aroma. That is why it’s oil is used to produce perfume and incense.
Acting As A Mulch
Many weeds act as a mulch for other crops, lowering the evaporation rate. Just prior to the reproduction period, these weeds need to be cut at the proper time.
Pest Control
That’s not all weeds’ benefits. Numerous scientific research supports the idea that weeds can help control pest populations. In general, weeds accomplish this by harboring pests’ natural enemies. For instance, in a study done in Switzerland, it was discovered that the presence of mugwort, tansy, and nettle between lettuce rows boosted the number of ladybirds and lacewings, which are crucial aphid predators.
List of Useful And Edible Weeds [5]
| Weeds species | Domestic use |
|---|---|
| Ageratum conyzoides | Medicine: Crushed leaves are used to heal wounds. Additionally used as a treatment for stomachaches. |
| Amaranthus spp. | Food: Amaranthus leaves of various species are consumed as a relish throughout East Africa, frequently combined with salt and groundnut paste. The flour made from the seed can be roasted and ground to make bread and biscuits. |
| Argemone mexicana | Other uses: Narcotic seeds make Tanzanian traditional beer more intoxicated. Seeds also have insecticidal qualities and can be toxic to animals. |
| Bidens pilosa | Food: Leaves and shoots are edible. Due to its abundance rather than its flavor, which is fairly aromatic, it is one of the weeds most frequently eaten as a famine meal. Medicine: The plant's juice can cure eye issues, and the leaves can be put into a poultice to treat wounds. Abdominal pain and diarrhea are treated using roots and stems. |
| Celosia spp. | Food: Leaves and inflorescence used as a vegetable and in soups and stews. |
| Chenopodium spp. | Medicine: In Zimbabwe, Chenopodium ambrosioides leaves are applied to the face to alleviate convulsions. A mixture of leaf powder and oil can also be applied directly to the skin to cure ringworm. |
| Commelina spp. | Commelina spp. |
| Corchorus spp. | Food: It is one of the most precious native veggies in hot, arid climates. Often cooked with potash. Medicine: Corchorus. olitorius can be used as a tonic to cure bladder, stomach, and toothaches. Other uses: Fibers can be woven to make course cloth. |
| Crotalaria spp. | Food: Some species' leaves and petals can be cooked and used as a relish, although to make it more pleasant, groundnut is frequently added. |
| Cynodon dactylon | Medicine: It is popular in Malawi as a treatment for heartburn and indigestion. Other uses: Pasture grass. |
| Cyprus esculentus | Food: Despite having a comparatively low protein content, tubers are twice as high in protein as cassava and are rich in starch, oil, phosphorus, and iron. In Zambia and Zimbabwe, tubers are used to produce porridge and can be consumed raw or roasted to make coffee. |
| Datura stramonium | Medicine: In Zimbabwe, leaves burned and smoke inhaled as a treatment for asthma. To treat ringworm, crushed leaves and seeds that contain the alkaloids hyoscine and atropine are combined with ghee. Crushed leaves can be used as an insect repellent. Other uses: In Malawi, it is a common belief that scattering leaves around the house will keep cockroaches away. Datura species are used as rat poison in stored grain. |
| Eleusine indica | Food: Seeds can be ground into flour and consumed as famine food in Zambia and Ethiopia. Medicine: Said to be a successful treatment for blood problems and coughs in Malawi. |
| Euphorbia heterophylla | Medicine: An infusion of roots and leaves can be used as a headache cure. |
| Euphorbia hirta | Medicine: Used to treat wounds by covering them with fresh leaves. |
| Galinsoga parviflora | Food: In some regions, leaves are eaten as a relish. |
| Gynandra gynandropsis | Food: It is one of the most well-liked sources of relish in East Africa. Cooked young shoots and leaves are frequently combined with pounded peanuts. Medicine: In Malawi, leaves are said to be a treatment for pneumonia. |
| Hibiscus cannabinus | Food: If the leaves are mashed with potash, they can be consumed as a relish during a famine. |
| Imperata cylindrica | Medicine: It is known as a remedy for digestive problems in Malawi. |
| Leucas martinensis | Medicine: Bracts and leaves are boiled in salt water, and the resulting infusion is drunk to treat throat infections. |
| Ocimum spp. | Medicine: A popular treatment for fevers. The essential oil of this plant acts as a mosquito repellent. |
| Oxygonum sinnuatum | Food: Occasionally cooked with potash to make a relish. Medicine: Widely used as a medicine. Crushed leaves are applied to the eyes to treat eye problems. Infusions of the root can be drunk to cure menstruation irregularities. |
| Physalis angulata | Food: Fruit can be eaten. It is a good source of vitamins A and C. Medicine: It is used to improve female fertility. |
| Potulacca olerecea | Food: Contains significant amounts of oxalic acid. It may be added to salads and soups, particularly in Mozambique and Malawi. Those with broad leaves that have been cooked and served as vegetables. Medicine: It is used as a snake bite remedy. |
| Schkuhria pinnata | Medicine: In Zimbabwe, gonorrhea is treated by consuming a leaf decoction. |
| Solanum nigrum | Food: Although the unripe fruit is deadly, the leaves are cooked and eaten as a relish in many regions of Africa. Medicine: Fruit juice has antifungal and antibacterial qualities. It is used to treat ringworm and other skin ailments. |
| Tagetes minuta | Medicine: To cure wound maggots, It is crushed in oil and applied to the skin. |
| Tribulus terrestris | Food: Leaves, shoots, and fruits are rich in calcium, iron, and vitamin C. Seeds can be ground to make flour, and Leaves can be used as salad. In periods of extreme food scarcity, fruits can be harvested and consumed. |
| Trichodesma zeylanicum | Medicine: Trichodesma physaloides Fengl powdered tuber is claimed to have aphrodisiac qualities. Intestinal worms are treated with an infusion of the roots and leaves. |
| Tridax procumbens | Medicine: The leaves are combined with other medicines to cure chest pain and coughing. |
| Triumfetta spp. | Medicine: The powdered root of Triumfetta welwitschia (Mat.) is used to prevent abortions in Zimbabwe. Triumfetta rhomboidea is also used to treat circumcision wounds by squeezing root juice into the wound. |
| Vernonia spp. | Medicine: Alkaloids found in leaves can be used to treat wounds. In Zimbabwe, the root is used to make infusions that treat infertility. Protection against body lice and insects can be achieved by applying leaves to the body. |
Disadvantages Of Weeds
The first image that springs to mind when you mention weeds is a useless plant that needs to be removed. So, the following are some typical disadvantages of weeds:
Reducing Crop Production
Weeds increase production costs in two ways: first, by lowering product quality and quantity, and second, by raising the input costs for weed control.
Agriculture yields are reduced when weeds compete with crops for water, nutrients, light, and space. As a result, the major crop’s yield is decreased.
Competition between weeds and crops can be disastrous. Weed population density (numbers per unit area), the timing of weed emergence in relation to the crop, and the percentage of resources (light, water, nutrients) absorbed by the weeds are all factors that influence how intensely weeds compete with crops.
Increasing Maintenance Cost
Weeds must be eliminated from the field because they are undesirable plants; this can be done either by using expensive weedicides or by laboriously uprooting the weeds by hand. Thus, it raises the maintenance cost for farmers.
Harmful To Human And Animals
Some weeds can even be fatal because they are toxic, can cause various skin issues and allergies, and are potentially harmful.
Noxious weeds have the potential to cause harm not just to humans but also to animals. They might also spread diseases because they are susceptible to getting sick themselves.
When milch animals eat certain weeds (Cleome viscosa), the milk will smell unpleasant. Sometimes death, illness, or deformity may be caused by weeds like Datura stramarium [6]
Decreasing Irrigation Efficiency
Another disadvantage of weeds is that they can compete with crops and prevent the main crops from absorbing the irrigated water, which inhibits the growth of the crops and plants. Such a phenomenon can decrease irrigation efficiency.
Interference In Water Management
Aquatic weeds impede water flow in canals, water transport systems, and drainage systems, making navigation challenging. They can deoxygenate the water and thereby kill the fish that live in it.
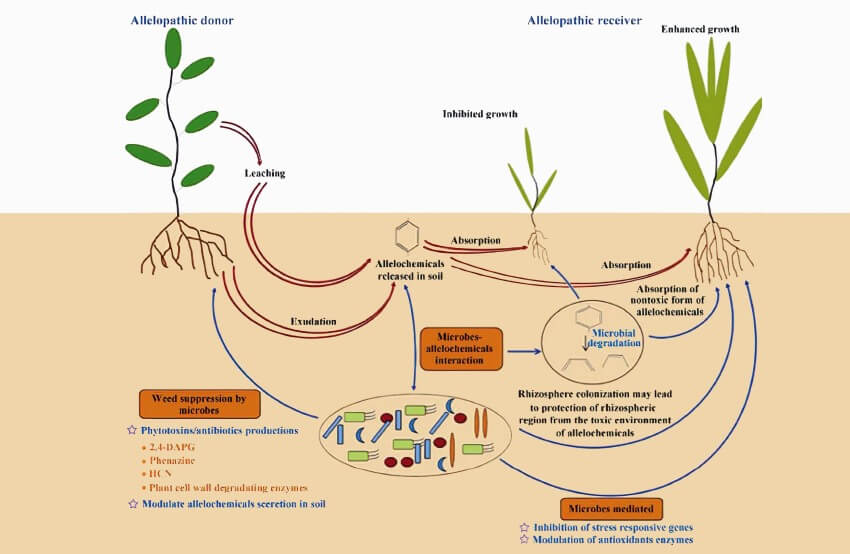
Causing Allelopathic effect
That’s not all disadvantages of weeds. In addition to these negative effects, weeds can release compounds harmful to crops, a condition known as allelopathy. Weed species may develop into effective competitors by producing phytotoxic natural compounds.
Allelochemicals are released into the environment by the donor plants through leachates, root exudates, and volatilization; thus, an accumulation of allelochemicals leads to toxicity, which affects crop growth and yield.
Some species that are transplanted into new settings may become weedy because they produce allelopathic compounds to which native plants are not yet adapted.
These substances may restrict the germination and growth of seeds and seedlings, as well as the growth of mature plants. It has been demonstrated that at least 50 different weed species can affect crops by producing allelopathic substances. However, It is challenging to prove a direct link, Since allelopathy typically develops through the complicated chemical structure of the soil.
Nutsedges, crabgrass, Canada thistle, and spotted knapweed are some weeds known to release allelochemicals that are hazardous to numerous crops. On the other hand, the allelopathic ability of several cultivated plants, particularly cover crops like winter rye, mustards Brassica spp., forage radish Raphanus sativus, and sorghum-sudangrass, can inhibit many weeds.
Source: Economic Importance of Weeds
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Weeds Overview
| Benefits Of Weeds | Drawbacks Of Weeds |
|---|---|
| Improving Soil Quality | Reducing Crop Production |
| Good For Wildlife | Increasing Maintenance Cost |
| Attracting Pollinators | Harmful To Human And Animals |
| Forage For Livestock | Interference In Water Management |
| Acting As A Mulch | Decreasing Irrigation Efficiency |
| Natural Medicine | Causing Allelopathic Effect |
| Pest Control | Reducing Land Value |
| Commercial Purposes | Reducing Pasture Palatability |